Abbot’s Flags
1943-1965
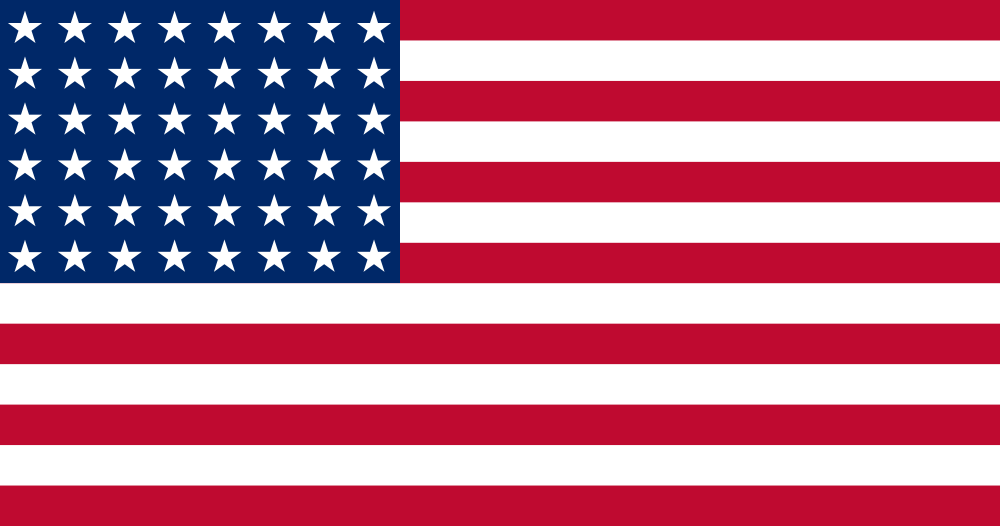
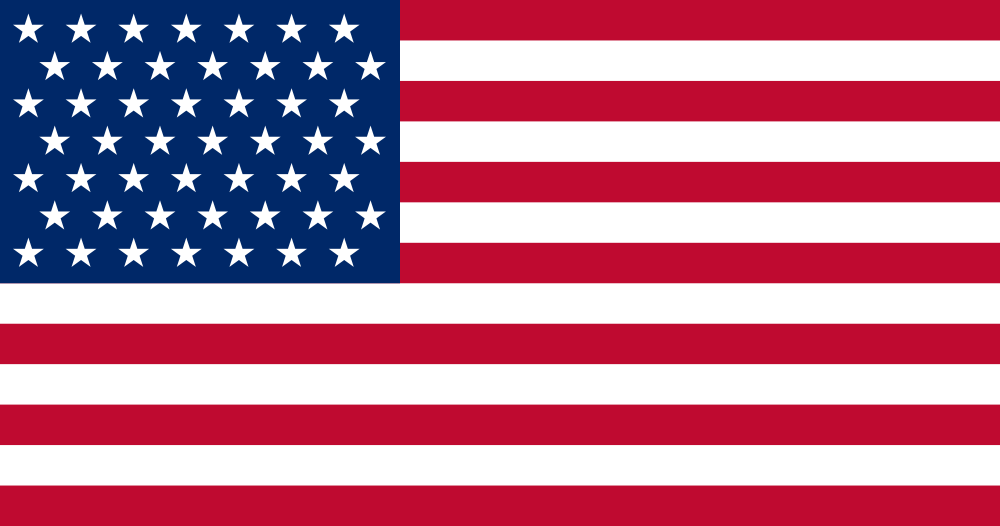
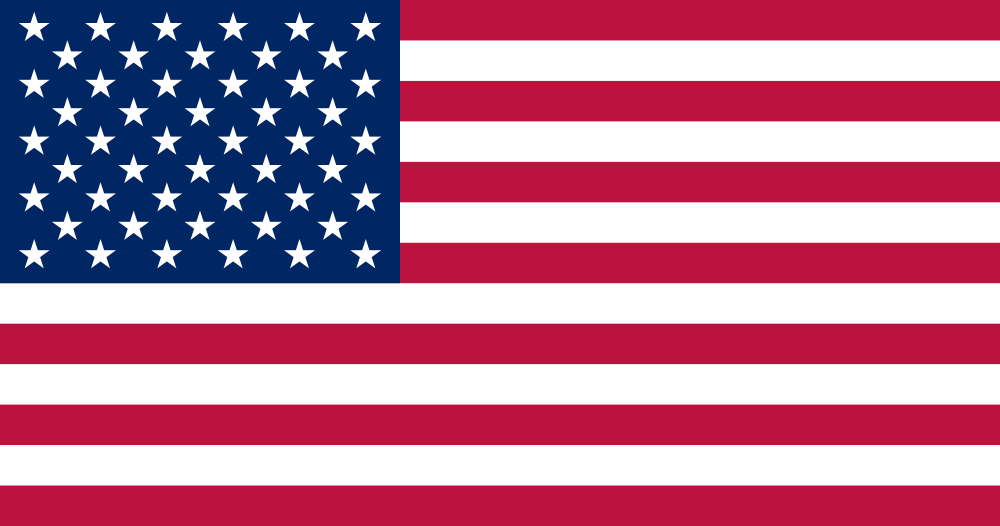
Abbot sailed under three American flags. The 48-star flag was flown in World War II and throughout most of the 1950s. When Alaska was admitted as a state, the 49-star flag was flown. After Hawaii was admitted a few months later, the 50-star flag was flown beginning in 1960.
The national flag, known in the navy as the ensign, was flown during daylight hours from the stern when in port. On a Fletcher-class destroyer at sea in World War II and the 1950s, the ensign was flown during daylight hours from a small “battle flagstaff” on the aft stack. The masts on Fletcher-class destroyers were modified shortly after World War II, and in the mid 1960s Abbot’s sea ensign was moved to the back of the tripod mainmast.
A jack signified that a ship was at anchor; it was flown only during daylight hours and was never displayed when the ship was underway. After the 9/11 attacks in 2001, the jack was changed to a Revolutionary War “Don’t Tread On Me” design.
The jack consisted of the blue field of the national flag, so when stars were added to the ensign they were also added to the jack. In addition, the jack was always the same size as the blue field of the ensign that was being displayed; this meant that for every size of American ensign aboard, a suitably sized jack was also kept.
A commission pennant signified that a vessel was an active United States warship. The commission pennant was flown day and night at the highest point on the mainmast, from the moment Abbot was commissioned until the moment it was decommissioned; it could only be displaced by the personal flag of an admiral or a senior civilian official, such as the president.
The commission pennant was quite small — it could be no larger than 2½ inches high and 6 feet long — and so it was virtually invisible among the mass of ropes and electronic gear in the upper mainmast.
In August 1945, Abbot returned to Puget Sound, Washington, flying a traditional homeward bound pennant from the mainmast. This looked somewhat like a commission pennant, but was much longer and had three stars; it was later cut up and divided among the crew.
The destroyer squadron and division pennants were flown only when the unit commander was aboard. Abbot served as a unit flagship in the 1950s and ’60s. The international maritime signal flags giving Abbot’s radio call sign (NIVW) were flown on the port side when entering or leaving a harbor, mainly for the practical reason of expediting communications between navy ships and civilian mariners and harbor staff.
 |
 |
 |
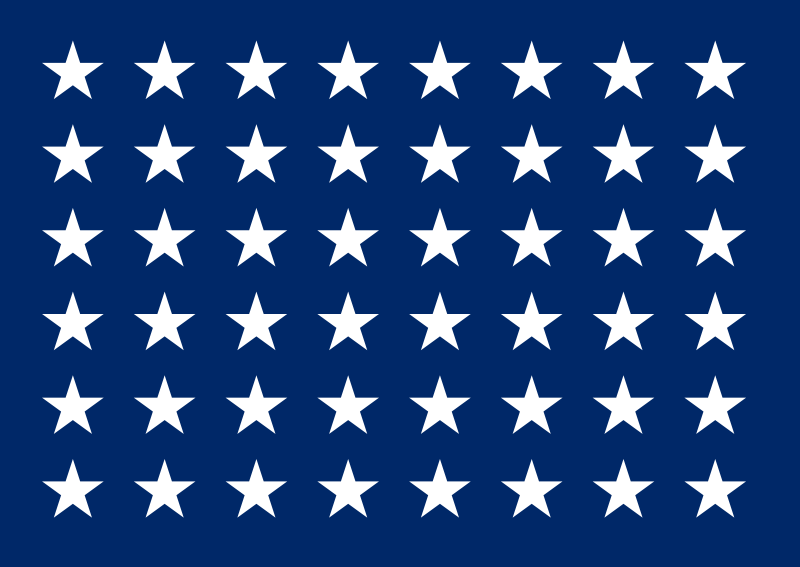 23 April 1943 — 3 July 1959 |
 4 July 1959 — 3 July 1960 |
 4 July 1960 — 26 March 1965 |
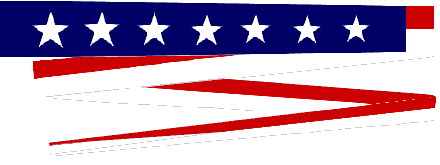 Commission Pennant |
||
 Destroyer Squadron 48 World War II |
 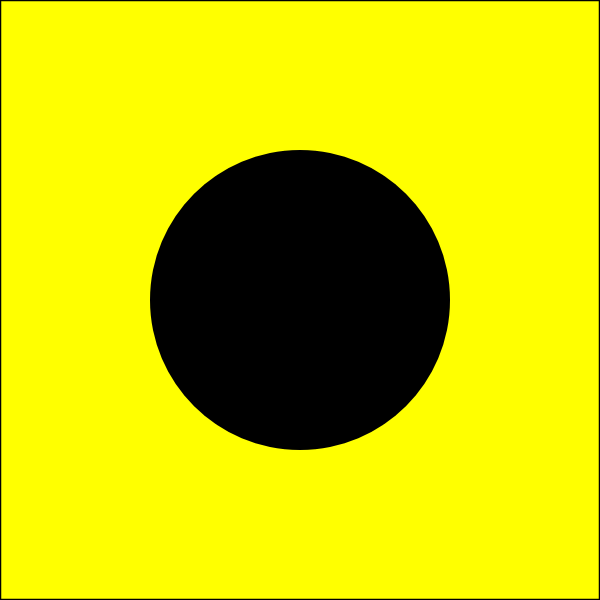   N-I-V-W Abbot’s radio call sign. |
 Destroyer Division 95 World War II |
Sources:
U.S. State Department
Sea Flags web site